Gravity Energy Storage Systems Market Report 2025: In-Depth Analysis of Technology Trends, Market Growth, and Strategic Opportunities. Explore Key Drivers, Regional Insights, and Competitive Dynamics Shaping the Industry.
- Executive Summary & Market Overview
- Key Technology Trends in Gravity Energy Storage Systems
- Competitive Landscape and Leading Players
- Market Growth Forecasts (2025–2030): CAGR, Revenue, and Volume Analysis
- Regional Analysis: Market Share and Emerging Hotspots
- Future Outlook: Innovations and Investment Opportunities
- Challenges, Risks, and Strategic Opportunities
- Sources & References
Executive Summary & Market Overview
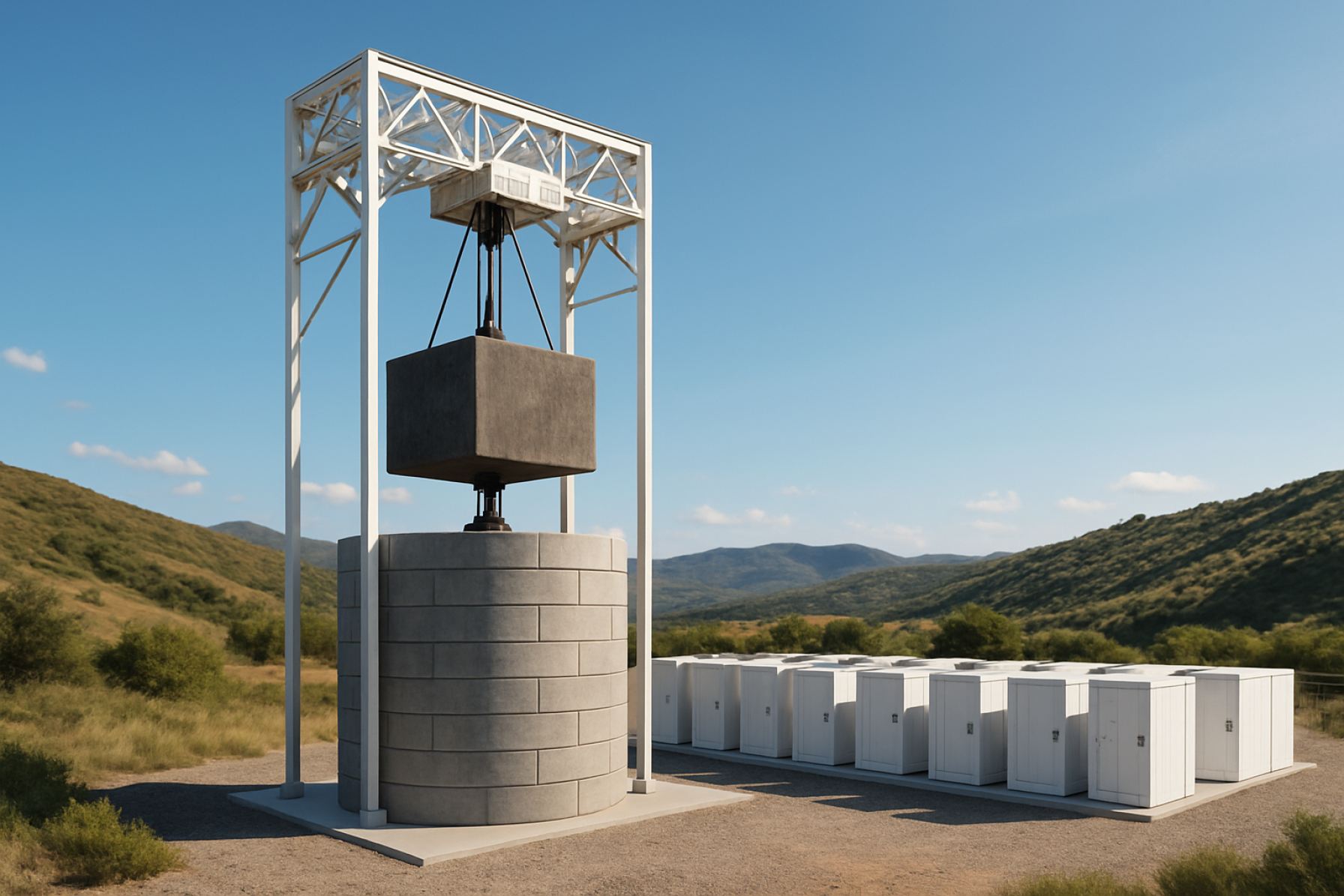
Gravity Energy Storage Systems (GESS) represent a rapidly emerging segment within the broader energy storage market, leveraging gravitational potential energy to store and release electricity. As the global energy sector accelerates its transition toward renewable sources, the need for scalable, long-duration storage solutions has intensified. GESS technologies, which typically involve lifting and lowering heavy masses to store and discharge energy, are gaining traction as a viable alternative to conventional battery storage, particularly for grid-scale applications.
In 2025, the global market for gravity energy storage systems is projected to experience robust growth, driven by increasing investments in renewable energy integration, grid modernization, and decarbonization initiatives. According to International Energy Agency, the worldwide installed capacity of energy storage is expected to more than double by 2030, with gravity-based solutions capturing a growing share due to their long operational lifespans, low environmental impact, and minimal reliance on critical minerals.
Key players such as Energy Vault, Gravitricity, and Heindl Energy are advancing commercial deployments and pilot projects across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. These companies are demonstrating the scalability and cost-effectiveness of GESS, with projects ranging from modular urban installations to large-scale systems capable of multi-hour to multi-day energy discharge. For instance, Energy Vault has announced several commercial agreements and is scaling up its EVx platform, while Gravitricity is piloting underground shaft-based storage in the UK and continental Europe.
Market drivers in 2025 include the increasing volatility of renewable generation, the need for grid resilience, and policy support for non-lithium storage technologies. The European Union’s Green Deal and the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act are catalyzing investment in innovative storage solutions, including gravity-based systems. However, challenges remain, such as high upfront capital costs, site-specific engineering requirements, and competition from established technologies like pumped hydro and advanced batteries.
Overall, gravity energy storage systems are positioned to play a significant role in the evolving energy storage landscape in 2025, offering a sustainable, long-duration solution that complements the rapid expansion of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Key Technology Trends in Gravity Energy Storage Systems
Gravity energy storage systems (GESS) are emerging as a promising solution for large-scale, long-duration energy storage, leveraging gravitational potential energy to store and release electricity. As of 2025, several key technology trends are shaping the evolution and commercial viability of GESS, driven by the need to support grid stability amid increasing renewable energy penetration.
- Advanced Mechanical Designs: Recent innovations focus on optimizing the mechanical components of GESS, such as modular block systems and high-efficiency winches. Companies like Energy Vault are pioneering multi-block architectures that enhance scalability and reduce construction costs, while also improving round-trip efficiency.
- Integration with Digital Control Systems: The adoption of AI-driven control platforms is enabling real-time optimization of energy dispatch and predictive maintenance. These digital solutions, as seen in projects by ABB, are crucial for maximizing system uptime and integrating GESS with smart grids.
- Material Innovations: The use of recycled and locally sourced materials for the construction of storage masses is gaining traction. This not only reduces the environmental footprint but also lowers capital expenditure. For example, Energy Vault utilizes composite blocks made from waste materials, aligning with circular economy principles.
- Hybridization with Other Storage Technologies: There is a growing trend toward hybrid systems that combine gravity storage with batteries or flywheels. This approach, highlighted in research by the International Energy Agency (IEA), allows for both rapid response and long-duration storage, enhancing grid flexibility.
- Underground and Vertical Shaft Solutions: To address land use constraints, companies like Gravitricity are developing underground gravity storage systems using disused mine shafts. These vertical solutions offer high energy density and can be deployed in urban or industrial settings.
These technology trends are underpinned by increasing investment and pilot projects worldwide, with the global GESS market expected to grow significantly through 2025 and beyond, according to Wood Mackenzie. As these innovations mature, gravity energy storage is poised to play a critical role in the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
Competitive Landscape and Leading Players
The competitive landscape for gravity energy storage systems (GESS) in 2025 is characterized by a mix of established energy technology firms, innovative startups, and strategic partnerships with utilities and grid operators. The sector is still emerging, but it is rapidly gaining traction as a viable alternative to chemical battery storage, particularly for long-duration and grid-scale applications.
Leading Players
- Energy Vault: Widely recognized as a pioneer in the field, Energy Vault has deployed its modular, crane-based gravity storage systems in several pilot and commercial projects worldwide. The company’s EVx platform, which uses composite blocks and proprietary control software, has attracted significant investment and partnerships with major utilities, including Enel and TALEN Energy. In 2024, Energy Vault announced new projects in the Middle East and Asia, further consolidating its global presence.
- Gravitricity: Based in the UK, Gravitricity focuses on vertical shaft-based gravity storage, utilizing disused mine shafts to lower and raise heavy weights. The company completed a successful 250kW demonstrator in Scotland and is now scaling up to multi-megawatt commercial systems. Gravitricity’s approach is particularly attractive for regions with legacy mining infrastructure.
- Heindl Energy: This German firm is developing a unique “rock piston” gravity storage concept, which involves lifting a massive rock cylinder to store energy. Heindl Energy has secured funding for pilot projects and is targeting markets with high renewable penetration and grid stability needs.
Market Dynamics
- Strategic Partnerships: Leading players are increasingly forming alliances with grid operators and renewable energy developers to integrate GESS into broader energy storage portfolios. For example, Energy Vault’s collaboration with Enel aims to demonstrate the scalability and cost-effectiveness of gravity storage in real-world grid applications.
- Investment and Funding: The sector has attracted substantial venture capital and government grants, with Energy Vault raising over $200 million in recent funding rounds and Gravitricity receiving support from the UK government’s energy innovation programs.
- Technology Differentiation: Companies are differentiating through proprietary control systems, modularity, and site adaptability. The ability to deploy systems in diverse geographies—urban, rural, or legacy industrial sites—is a key competitive factor.
As of 2025, the gravity energy storage market remains relatively concentrated, but new entrants and technology advancements are expected to intensify competition and drive down costs, positioning GESS as a critical component of the global energy transition.
Market Growth Forecasts (2025–2030): CAGR, Revenue, and Volume Analysis
The global gravity energy storage systems (GESS) market is poised for robust growth between 2025 and 2030, driven by increasing investments in renewable energy integration and the urgent need for scalable, long-duration energy storage solutions. According to projections by IDTechEx, the GESS market is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 35% during this period, outpacing many other energy storage technologies due to its unique advantages in cost, scalability, and environmental impact.
Revenue forecasts indicate that the global GESS market could surpass $2.5 billion by 2030, up from an estimated $400 million in 2025. This surge is attributed to the commissioning of large-scale projects in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific, where grid operators and utilities are seeking alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for long-duration storage. Notably, the European market is anticipated to lead in revenue share, propelled by supportive regulatory frameworks and ambitious decarbonization targets set by the European Commission.
In terms of installed capacity, the cumulative global volume of gravity energy storage is projected to grow from less than 1 GWh in 2025 to over 10 GWh by 2030. This expansion will be driven by the deployment of both new-build vertical tower systems and the repurposing of existing mine shafts, as demonstrated by projects from companies such as Energy Vault and Gravity Energy AG. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and Australia, is expected to witness the fastest capacity growth, supported by government incentives and the rapid scaling of renewable energy assets.
- CAGR (2025–2030): ~35% globally
- Revenue (2030): $2.5 billion (projected)
- Installed Capacity (2030): >10 GWh worldwide
Key market drivers include the declining levelized cost of storage (LCOS) for gravity-based systems, increasing grid reliability requirements, and the growing need for sustainable, non-chemical storage alternatives. As the technology matures and more pilot projects transition to commercial operation, the GESS market is expected to solidify its role as a critical enabler of the global energy transition.
Regional Analysis: Market Share and Emerging Hotspots
The regional landscape for Gravity Energy Storage Systems (GESS) in 2025 is characterized by a dynamic interplay of market share distribution and the emergence of new hotspots driven by policy support, grid modernization, and renewable integration. Europe continues to lead the global GESS market, accounting for an estimated 38% of installed capacity, propelled by ambitious decarbonization targets and robust investment in grid flexibility. Countries such as Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom are at the forefront, leveraging GESS to complement intermittent renewables and enhance energy security. Notably, Switzerland’s deployment of underground gravity storage projects has set a benchmark for technical innovation and regulatory alignment in the region (International Energy Agency).
North America, particularly the United States, holds approximately 27% of the global GESS market share in 2025. The region’s growth is underpinned by state-level incentives, the retirement of aging fossil fuel plants, and the need for long-duration storage to support ambitious renewable portfolio standards. California and Texas have emerged as key states, with pilot projects demonstrating the scalability and cost-effectiveness of gravity-based storage compared to lithium-ion alternatives (U.S. Department of Energy).
Asia-Pacific is rapidly evolving as an emerging hotspot, with China and Australia making significant strides. China’s focus on grid resilience and its “new energy storage” policy framework have catalyzed investments in both above-ground and underground gravity storage solutions. Australia, facing grid stability challenges due to high solar and wind penetration, is piloting GESS projects in remote and mining regions, aiming to reduce reliance on diesel and enhance off-grid reliability (Wood Mackenzie).
- Europe: Market leader with advanced regulatory support and integration with renewables.
- North America: Strong growth in the U.S., driven by policy and grid modernization needs.
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing region, with China and Australia as innovation centers.
Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East are also showing early-stage activity, particularly where grid expansion and renewable integration are priorities. As technology costs decline and project financing becomes more accessible, these regions are expected to contribute to the next wave of GESS adoption (BloombergNEF).
Future Outlook: Innovations and Investment Opportunities
Looking ahead to 2025, gravity energy storage systems (GESS) are poised for significant innovation and investment, driven by the global push for decarbonization and the increasing integration of renewable energy sources. As grid operators seek reliable, long-duration storage solutions to balance intermittent solar and wind generation, GESS technologies are emerging as a promising alternative to conventional battery storage, particularly in regions with suitable topography or existing infrastructure.
Key innovations expected in 2025 include advancements in modular design, automation, and digital control systems. Companies such as Energy Vault are developing next-generation systems that utilize composite blocks and AI-driven software to optimize energy dispatch and storage cycles. These improvements are anticipated to enhance round-trip efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and enable more flexible deployment in both urban and remote settings.
Investment opportunities are expanding as governments and private investors recognize the potential of GESS to provide grid stability and support renewable integration. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that global investment in energy storage could surpass $20 billion by 2025, with a growing share allocated to non-battery technologies such as gravity-based systems. Notably, the European Union’s Green Deal and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Long Duration Storage Shot are catalyzing pilot projects and commercial deployments, creating a favorable policy environment for GESS innovation.
- Urban and Industrial Applications: Innovations in vertical storage towers and retrofitting of decommissioned mine shafts are opening new markets for GESS in densely populated and industrialized areas, as demonstrated by pilot projects in Switzerland and the United Kingdom (Energy Storage News).
- Hybrid Systems: Integration with other storage and generation technologies, such as pumped hydro and solar PV, is being explored to maximize system flexibility and economic returns (Wood Mackenzie).
- Cost Reductions: Ongoing R&D is focused on using recycled materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to lower capital expenditures, making GESS more competitive with lithium-ion batteries over the system lifetime (BloombergNEF).
In summary, 2025 is set to be a pivotal year for gravity energy storage systems, with technological breakthroughs and supportive investment climates accelerating their path toward commercial viability and large-scale deployment.
Challenges, Risks, and Strategic Opportunities
Gravity Energy Storage Systems (GESS) are emerging as a promising solution for large-scale, long-duration energy storage, leveraging gravitational potential energy to store and release electricity. However, as the sector moves toward commercialization in 2025, it faces a complex landscape of challenges, risks, and strategic opportunities.
Challenges and Risks
- High Capital Expenditure: GESS projects require significant upfront investment for infrastructure, including heavy lifting equipment, robust structural components, and site preparation. This can deter investors compared to more established storage technologies like lithium-ion batteries (International Energy Agency).
- Site Constraints: The physical footprint and geological requirements for GESS—such as the need for vertical shafts or tall structures—limit deployment to suitable locations. Urban and densely populated areas may not be viable, restricting market potential (U.S. Department of Energy).
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: Novelty and scale of GESS can lead to lengthy permitting processes, as regulatory frameworks are often tailored to conventional storage or generation assets. This can delay project timelines and increase costs (International Renewable Energy Agency).
- Technology Maturity: While pilot projects by companies like Energy Vault and Gravity Energy AG have demonstrated feasibility, large-scale commercial deployments remain limited. Uncertainties around long-term performance, maintenance, and scalability persist.
Strategic Opportunities
- Grid Decarbonization: GESS can provide long-duration storage critical for integrating variable renewables, supporting grid stability, and reducing reliance on fossil-fuel peaker plants. This aligns with global decarbonization targets and creates opportunities for policy-driven growth (International Energy Agency).
- Cost Declines Through Scale: As more projects are deployed and supply chains mature, costs are expected to decrease, improving competitiveness with other storage technologies (BloombergNEF).
- Hybridization and Co-location: GESS can be co-located with renewable generation or other storage assets, offering flexible, multi-service value streams such as frequency regulation, capacity, and ancillary services (U.S. Department of Energy).
- Emerging Markets: Regions with limited access to pumped hydro or battery supply chains may find GESS an attractive alternative, especially where local materials and labor can be leveraged.
In summary, while GESS faces notable technical, financial, and regulatory hurdles in 2025, its strategic alignment with the energy transition and potential for cost reduction position it as a key contender in the evolving energy storage landscape.
Sources & References
- International Energy Agency
- Energy Vault
- Gravitricity
- Heindl Energy
- ABB
- Wood Mackenzie
- Enel
- TALEN Energy
- IDTechEx
- European Commission
- Gravity Energy AG
- BloombergNEF
- Energy Storage News